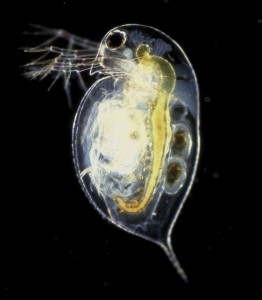
Although there are other species, Daphnia pulex comes to mind when one thinks of the water flea. The tiny crustacean. D. pulex is cosmopolitan. That word means it is found throughout the cosmetic (surface) layer of the planet.
The National Institutes of Health informs us that the water flea is “a versatile model system to investigate” biological systems. Also to investigate matters such as immunity, disease, and cellular function.
Appearance Variability
The image with this article, reveals the great beauty of this tiny creature. Enjoy this instructive one minute video. Another video, one-half minute in length, displays daphnia in an aquarium.
The water flea’s name comes from its appearance and jerky motions controlled by its antennae. These resemble arms with extended fingers. Other than the overall shape and these appendages, the outstanding feature of D. pulex is its eye-like ocellus.
Although a favored environment is shaded ponds, D. pulex also thrives in deep lakes. Its environment determines its appearance. It displays little pigmentation, when light is minimal. In bright areas, daphnia of color abound. There is even a red version – due to the presence of hemoglobin.
Environment and Reproduction
D. pulex swims freely in open water. But it is often intermingled with vegetation. It cannot survive in strong currents. The water flea may engage in sexual reproduction, but no male is required to reproduce. When no male participates in the process, reproduction is by parthogenesis.
Daphnia consumes phytoplankton as food. It may move vertically up or down a column of water, whether to obtain food or to avoid predators. Frequently, the critters are found higher in the water column at night.
Purchase Daphnia?
Why is the water flea available commercially? For one thing, hobbyists and fish farmers purchase it as food for small fish and fish “fry.” The creature rarely constitutes a complete diet, as it possesses laxative properties. In addition, another species, D. magna, is useful in determining aquatic effluent quality.
Note: You might also enjoy The Eight-Legged Tardigrade or Water Bear
References:
← Back to Classic Science
← Home

I used to see water fleas in pond water when I studied biology. They are beautiful. I wonder whether they could serve as a source of food for humans?
Surely you jest! You do jest, don’t you? You’re not kidding… Oh. 🙂